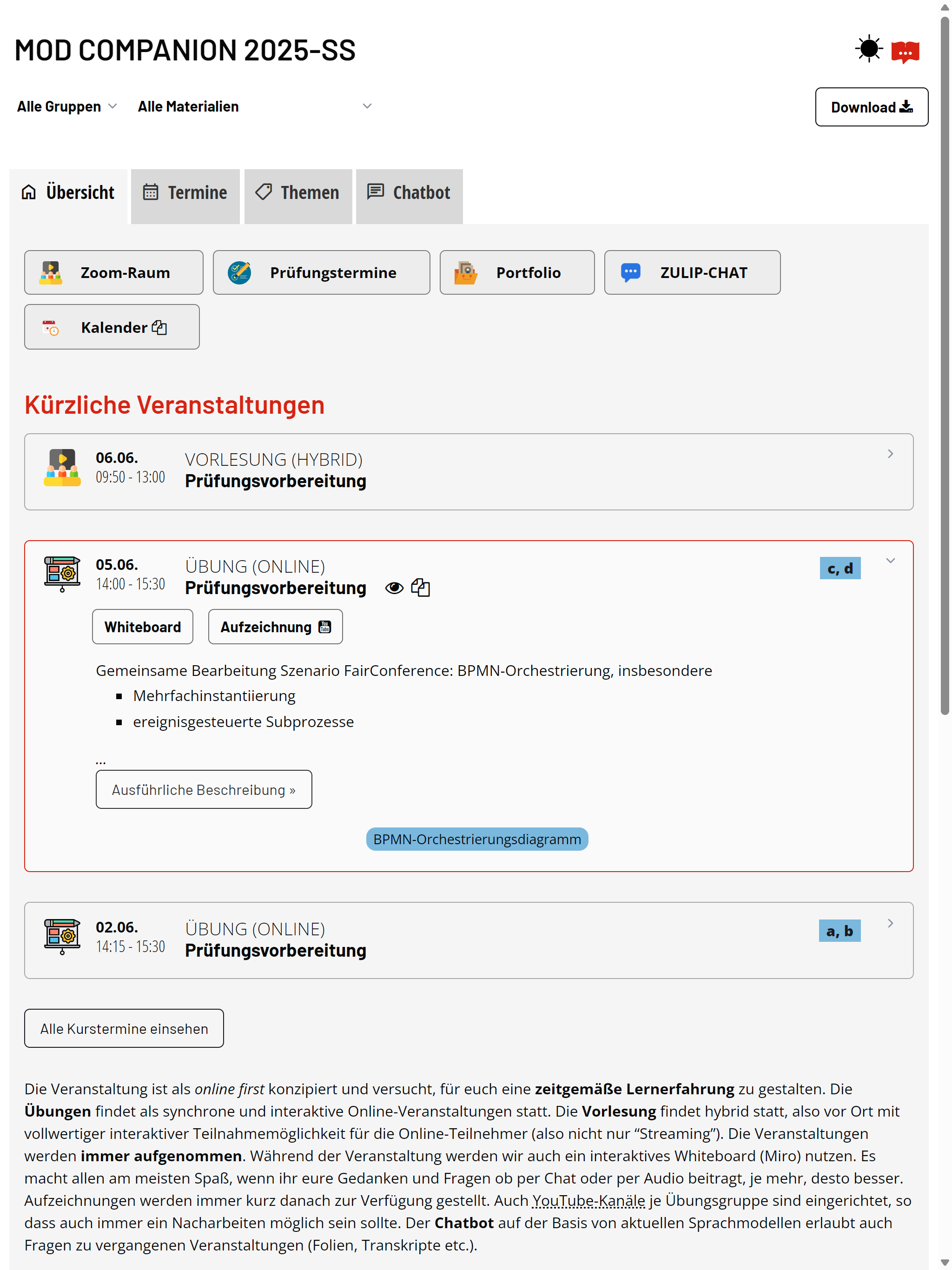
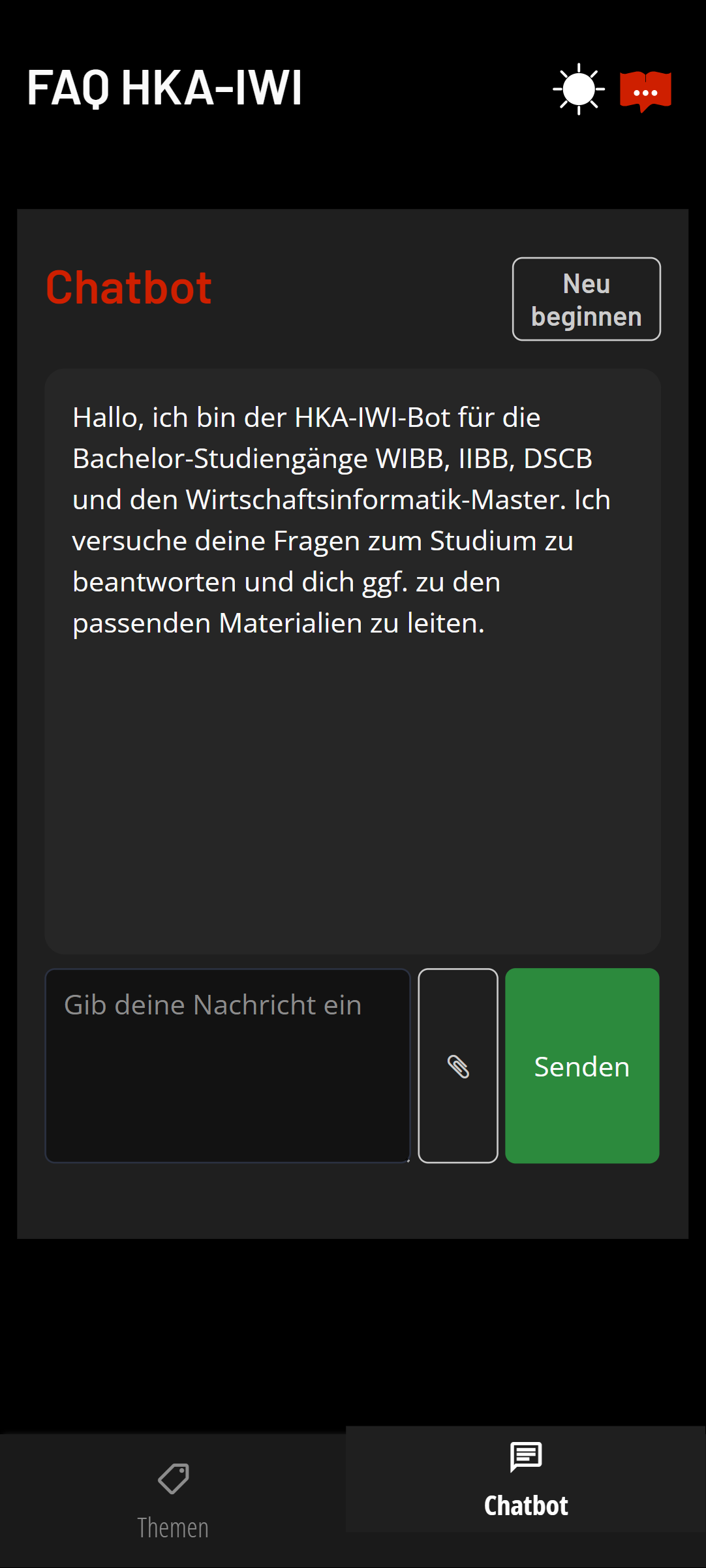
The Learning Companion is designed as companion for online-centered learning, supporting both synchronous and asynchronous participation, both in-person, mixed, or hybrid learning settings.
Learning in the 21st century is not about scarcity, but about abundance. Its not just about slides and lecture notes, but also about whiteboards, recordings, learning videos, and curated content like books, blog entries, or YouTube videos.
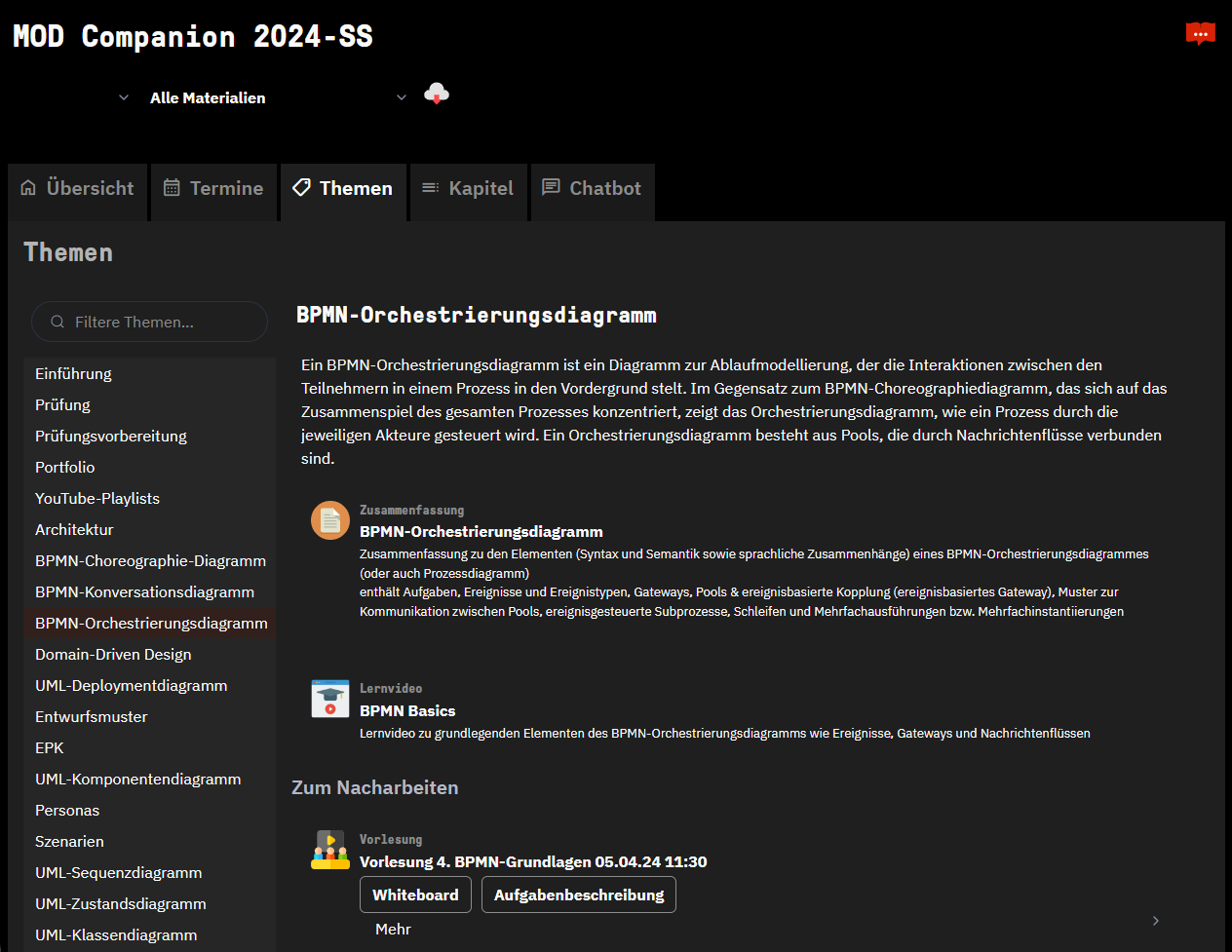
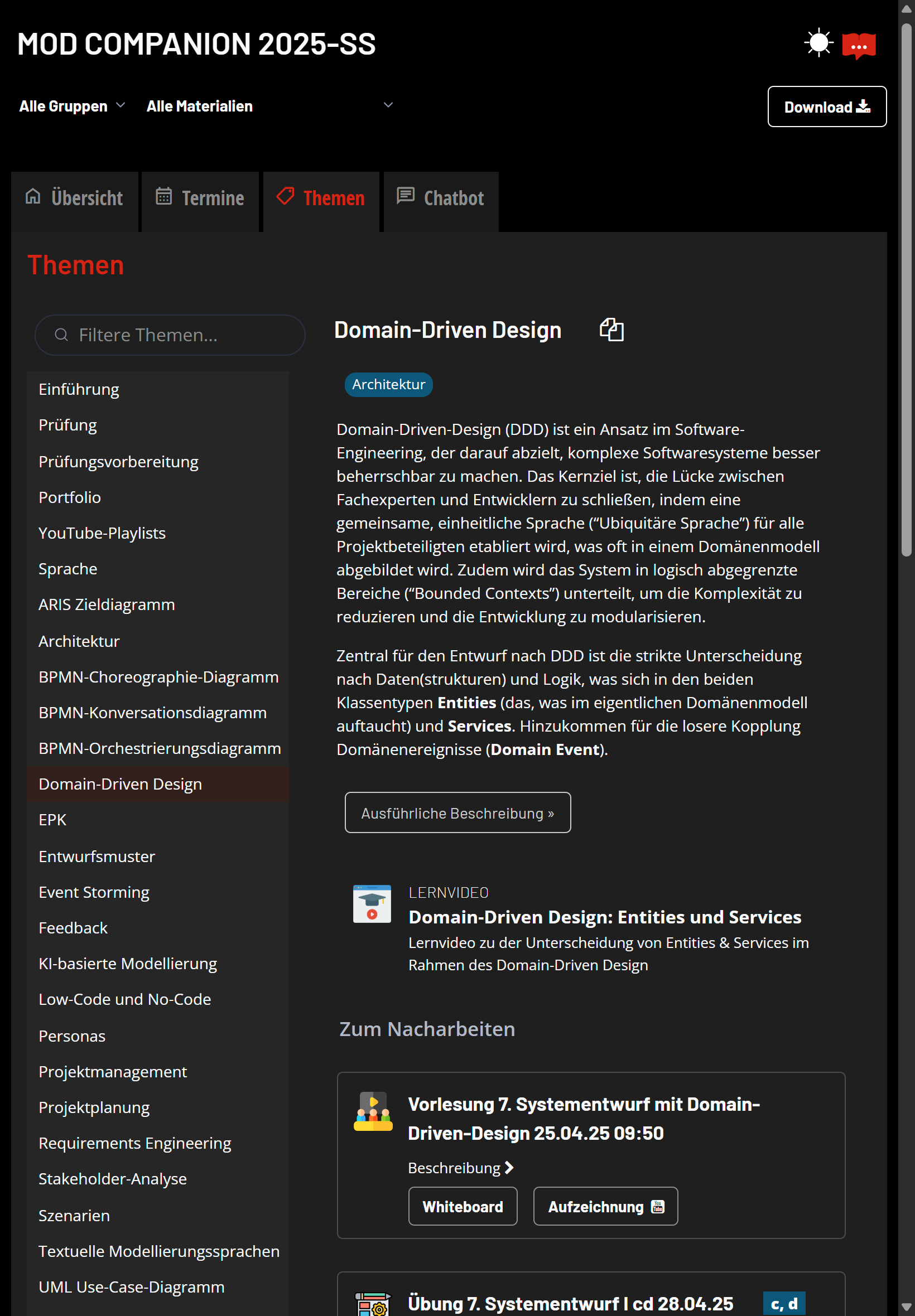
Design learning experience is about creating opportunities for learners to engage with the content, not about managing learning. The companion supports integrating materials for exploration, preparation, repetition, and reflection. It supports timeline-based, topic-based, structure-based, and conversational access to all the materials. Views can be embedded, e.g., into whiteboards.
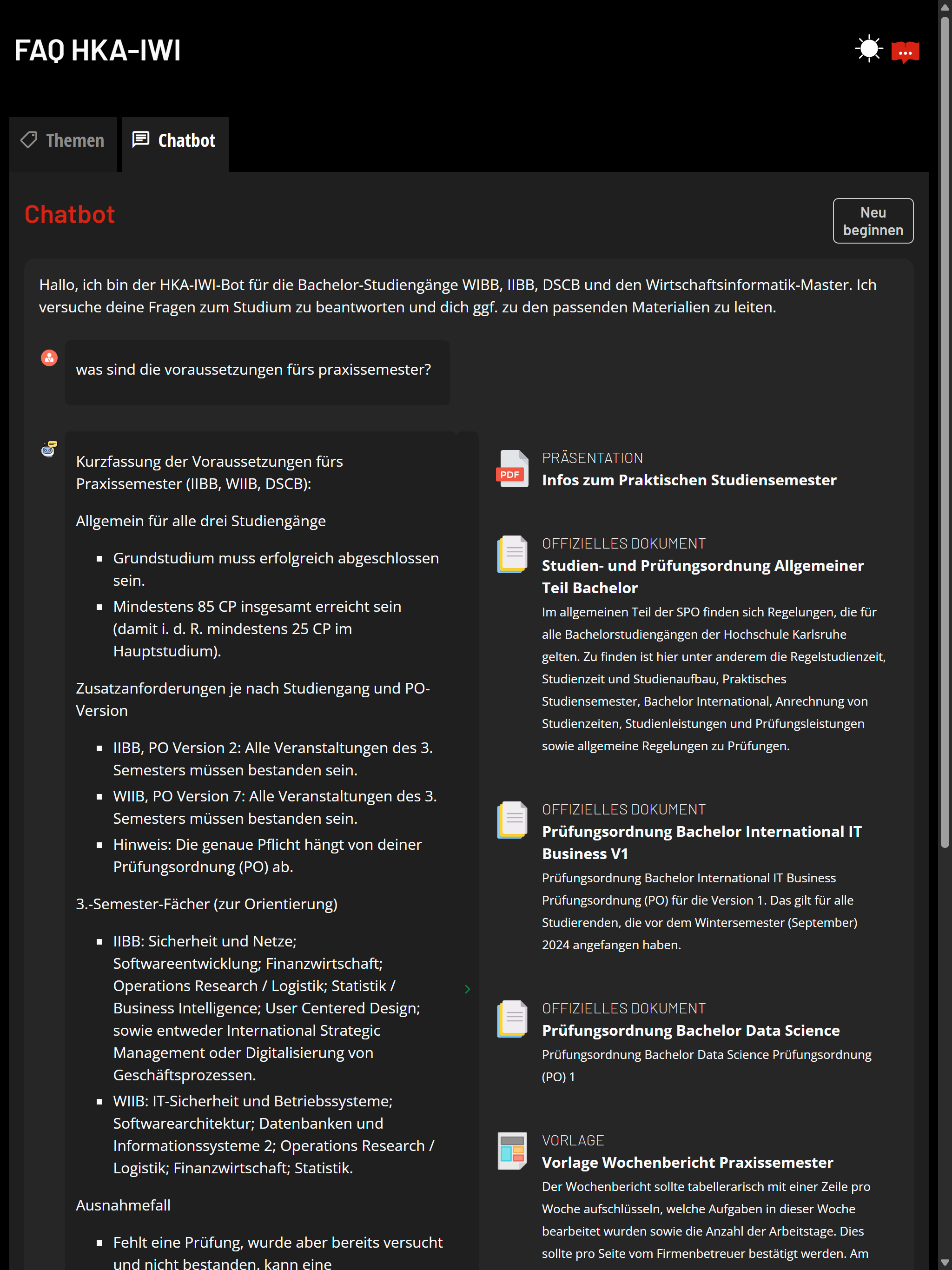
Based on the content of the supplied materials, ranging from transcripts to web resources, an LLM-based chatbot with agentic capabilities will be able to answer, provide additional information, and provide course-specific tools and support. Comprehensive observability and self-evaluation capabilities simplify continuous improvement.
Using a headless CMS and preferring convention over configuration, the Learning Companion is designed to be lightweight and efficient for the teacher. Many aspects, including the chatbot interface, can be easily fine-tuned to achieve the best possible learning experience.
The Learning Companion is designed to be cloud-native, using scalable object storage for all the materials, stateless container(s) for the backend functionality with easy loadbalancing, and a headless CMS for managing the course data.
Course model
The Learning Companion uses a flexible model with feature flags. It supports
- A timeline-based view on course slots with concrete dates, complemented by an optional milestone-view for accompanying projects
- A topic-based view on all the provided materials and course slots.
- A structural view putting the whole course into a more traditional table of contents
- Conversational view using a state-of-the-art LLM-based chatbot
Content management
- Easy to use admin backend
- Extensive use of convention over configuration to reduce the effort of creating and maintaining content
- Flexible and extensible use of scalable object storage as a native store
- AI-generated summaries (e.g., based on transcripts) and other AI-enhanced workflows
- Integration with Wordpress-based CMS for student-generated content
Chatbot features
- Supports a wide variety of LLMs; the model to be used can be configured on a course and agent level (OpenAI and all compatible models - including self-hosted ones, especially gpt-oss, but also qwen, Google, Anthropic, DeepSeek), including reasoning models like GPT-5, or Gemini 3-Pro and their respective parameters
- Querying indexed documents (with metadata), implementing a RAG approach with per-course configuration of major parameters (like number of chunks)
- Token streaming to the UI for low-latency answers
- Configurable history management with no required account creation (and thus privacy friendly)
- Generate topic suggestions
- Generate follow-up question suggestions
- Inline citations of the used materials for better traceability (with direct quotes)
- Multiple and configurable agents (in CMS) chosen at runtime (previously dynamic prompt selection) (either via LLM or direct similarity search), including a customized set of tools for each agent
- Sidebar with suggested course materials relevant to the question
- Thumbs voting to improve the quality
- Extensive chatbot interaction logging and self-evaluation via LLM-as-a-judge
- Generate clarifying info prompts to the user
- Specialized tools (or functions) using an agentic workflow to make the LLM automatically choose what to include - especially useful for API-based integration of content such as timetables, staff directories, meal plans, etc.
- Low-barrier improvement via directly supported Q&A
- Upload of images and other files as multimodal input
- Support for reasoning summaries for "thinking" models
Flexible document indexing
- Wide range of documents such as pdf, md, docx, pptx, but also video transcripts (both vtt and YouTube)
- Periodic indexing of web sites and other content
- Observability of workflow execution
- Multiple indexing methods, including multimodal indexing
- Configurable indexing parameters, such as chunking strategy
- Easy reindexing and chunk inspection from the CMS
Evaluation and quality monitoring
- Anonymous logging
- Self evaluation using LLM-as-a-judge approaches
- Manual quality tagging and annotation for improvement
- Auto-expiring information (e.g., semester-related)
Extensible and customizable
- Many feature flags, supporting, e.g., synchronous courses (with timeline), asynchronous courses, or course-independent bots
- Themeable, supporting automatic and manual switching between light and dark mode
- Easy addition of new material types
- Supports multiple languages (or a course level)
- Models, prompts, agents, functions and their parameters directly configurable in CMS
- Extensive API and views designed to be embedded into other sites (fragments and OEmbed)
- Support for MCP clients and servers, support for A2A protocol
- Webhooks and AMQP/RabbitMQ messaging for event-driven workflows (e.g., for workflows in n8n)
- Soon: compose chatbots from multiple courses or more specialized bots
Specialized features for supporting modelling courses
- Generate UML class diagrams, use case diagrams, sequence diagrams, state charts, component and deployment diagrams via PlantUML and inline display, including direct editing
- Generate ARIS EPC and Goal Diagrams via draw.io, including inline display
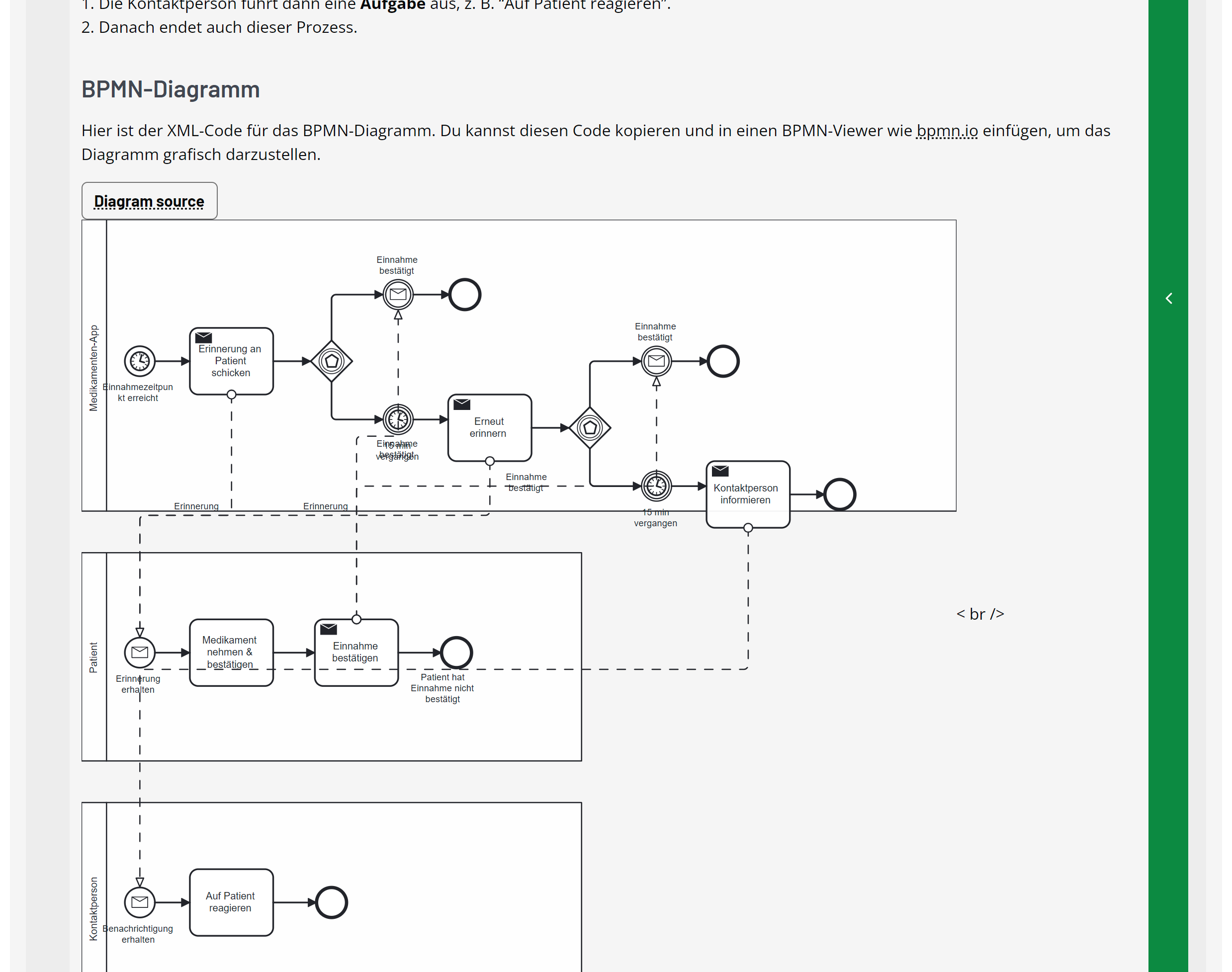
- Generate BPMN Process and Conversation Diagrams using BPMN-XML (for bpmn.io) and drawio syntax, including inline display and direct editor connection
- Generate ER-Diagrams (Chen notation) using draw.io
- Feedback on UML, BPMN, and ARIS diagrams uploaded by students, based on course-specific good practices
- Suggested improvement presented as a diagram
- Integrated editors for BPMN processes and PlantUML-based diagrams, directly linked to the chatbot
Modern technologies
- FastAPI with Jinja2 (with JinjaX components) and extensive use of Pydantic
- Request handling and service invocation completely asynchronous, maximizing throughput
- Hypermedia-first approach using HTMX, complemented by AlpineJS
- Responsive web design
- Built ontop of Pydantic AI
- Prefect as orchestrator for indexing tasks
- Weaviate as a vector database
- PostgreSQL history management
- Log observability with OTEL and Pydantic's LogFire, GenAI observability with LangFuse (self-hosted)
- Complemented by n8n workflows for contextualized automations via the API
Team
- Ghita Kristiansen
concept for a learning companion providing consultancy on UX methods - Ralitsa Atanasova
POC for a new approach to providing course materials - Marcelo Günther Farah
POC for generating diagrams for a modelling course - Luka von Ahn
analysis of user-centered techniques for bot quality assurance, implementation and evaluation of a bot for the economics department - Athanasia Skaroglou-Chasioti
context disambiguation, implementation and evaluation of a bot for the computer science and business information systems department - Hümeyra Azal
Analysis of accessibility and suggestions for improvement - Hai-Mi Nguyen
feedback on modelling diagrams, multimodal input - Andreas P. Schmidt
main developer, project coordinator